 |
After experimenting with AI image generation, you may start to wonder how it works.
 |
 |
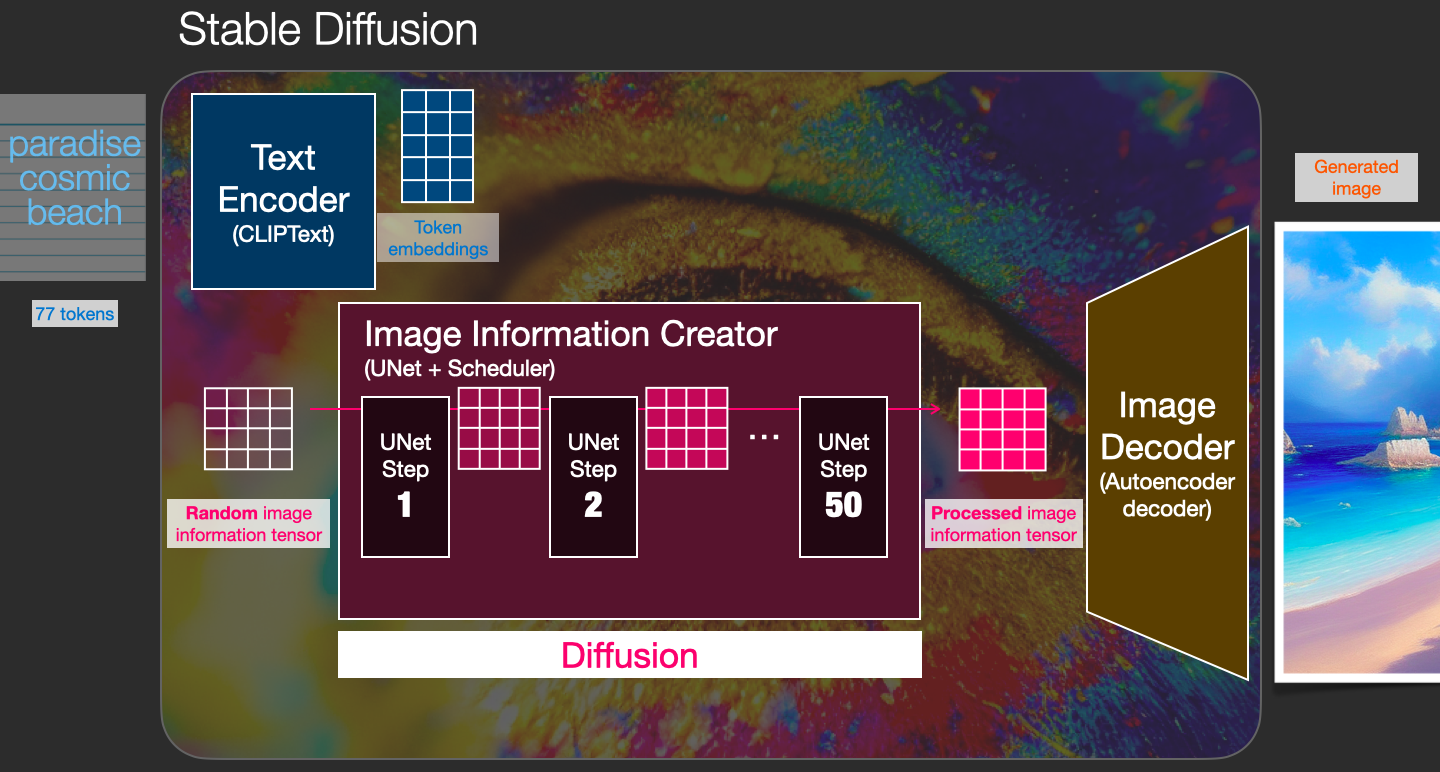
Stable Diffusion is a system made up of several components and models. It is not one monolithic model.
As we look under the hood, the first observation we can make is that there’s a text-understanding component that translates the text information into a numeric representation that captures the ideas in the text.
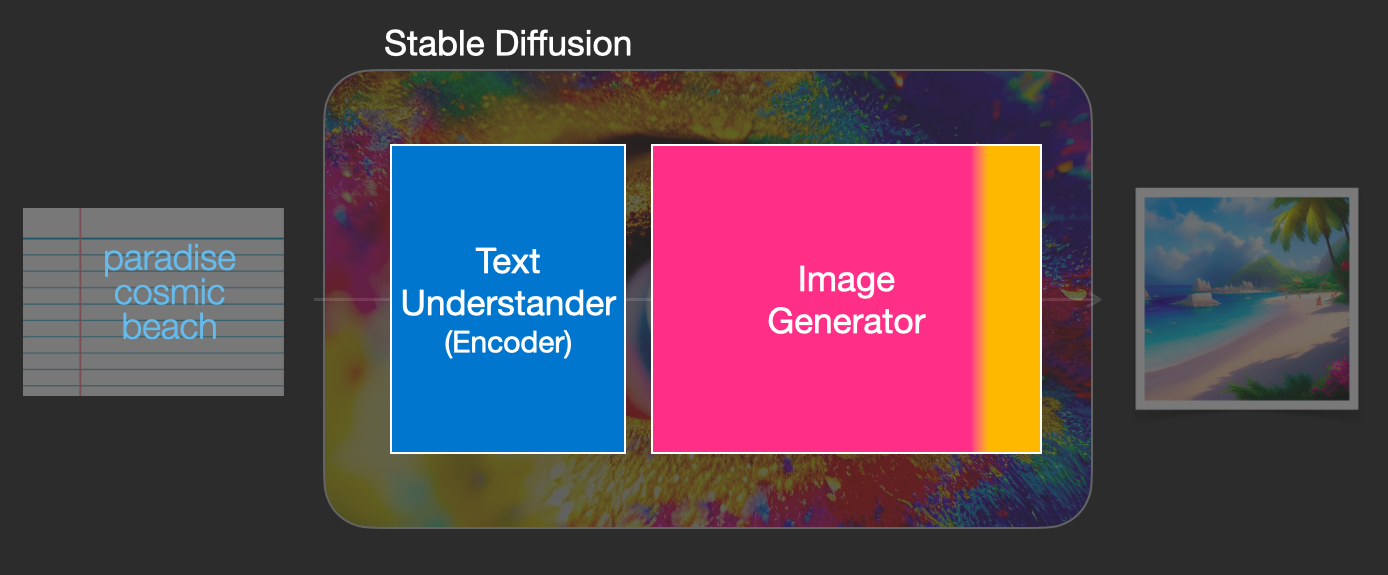 |
We’re starting with a high-level view and we’ll get into more machine learning details later in this article. However, we can say that this text encoder is a special Transformer language model (technically: the text encoder of a CLIP model). It takes the input text and outputs a list of numbers representing each word/token in the text (a vector per token).
That information is then presented to the Image Generator, which is composed of a couple of components itself.
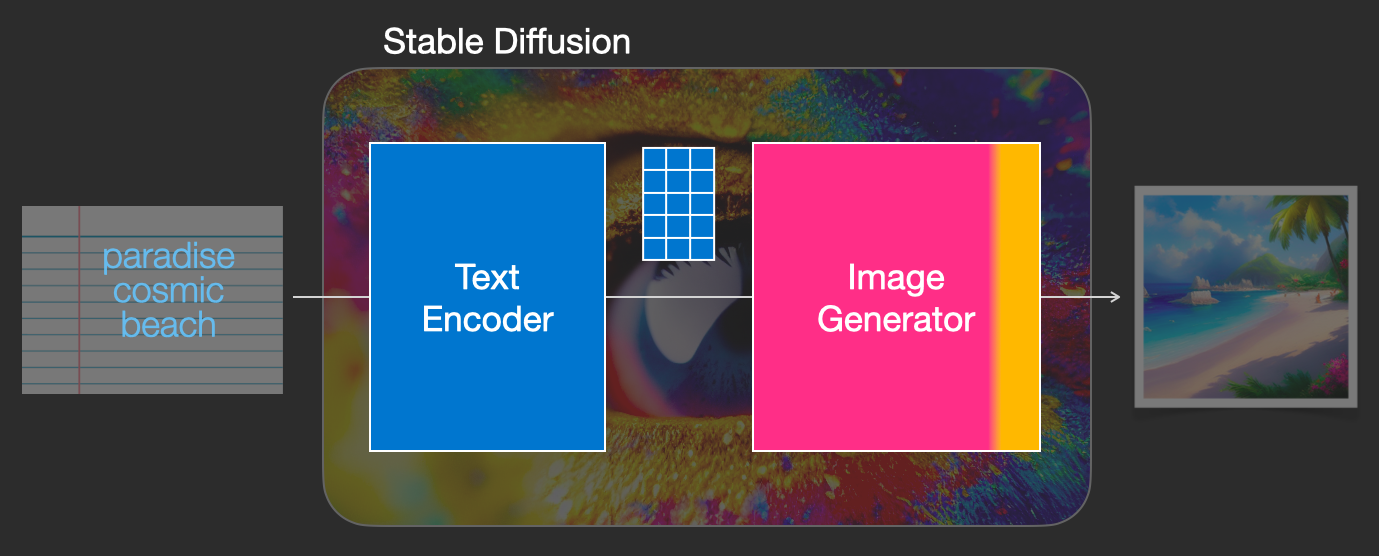 |
The image generator goes through two stages:
1- Image information creator
This component is the secret sauce of Stable Diffusion. It’s where a lot of the performance gain over previous models is achieved.
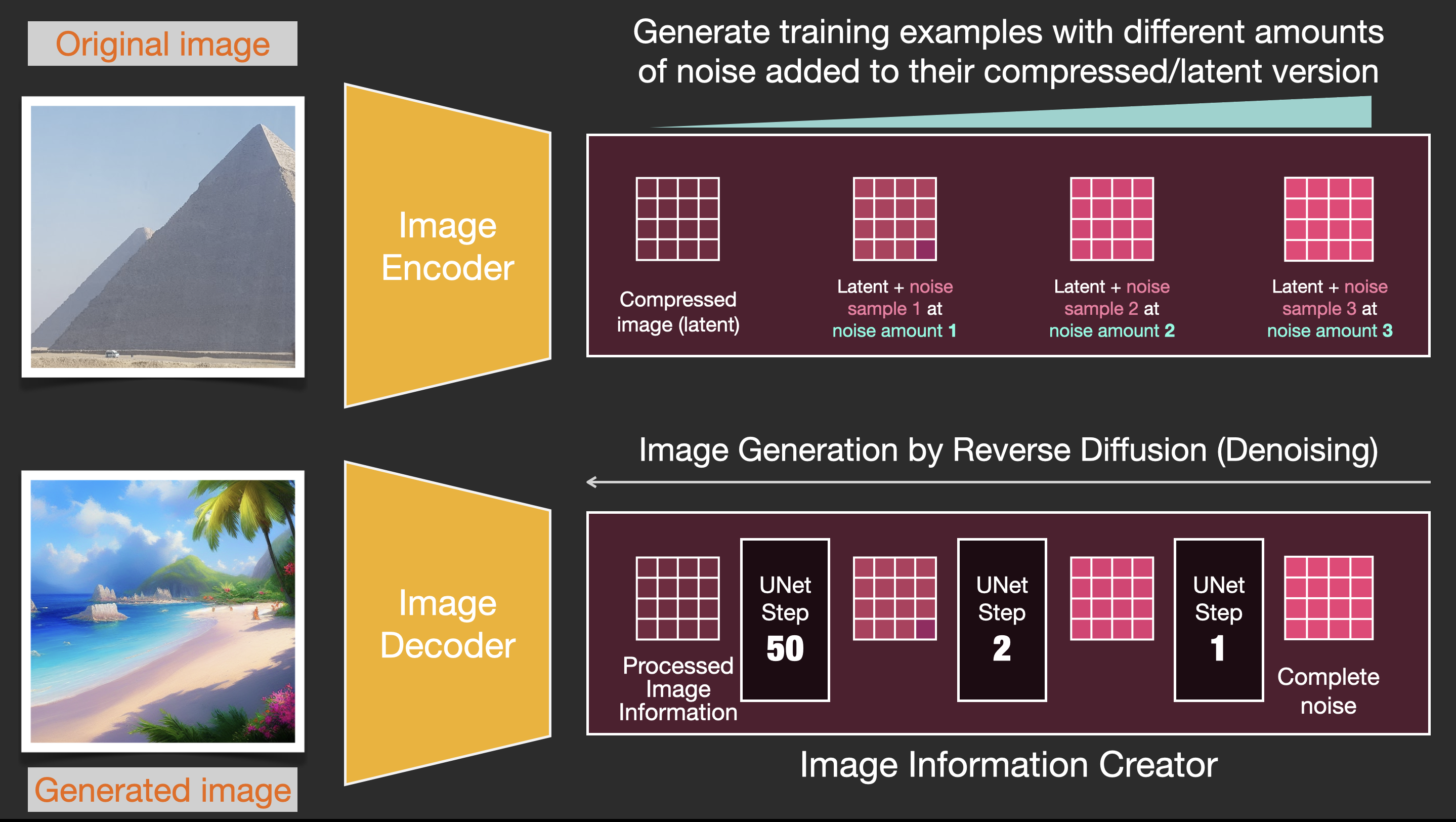
This component runs for multiple steps to generate image information. This is the steps parameter in Stable Diffusion interfaces and libraries which often defaults to 50 or 100.
The image information creator works completely in the image information space (or latent space). We’ll talk more about what that means later in the post. This property makes it faster than previous diffusion models that worked in pixel space. In technical terms, this component is made up of a UNet neural network and a scheduling algorithm.
The word “diffusion” describes what happens in this component. It is the step by step processing of information that leads to a high-quality image being generated in the end (by the next component, the image decoder).
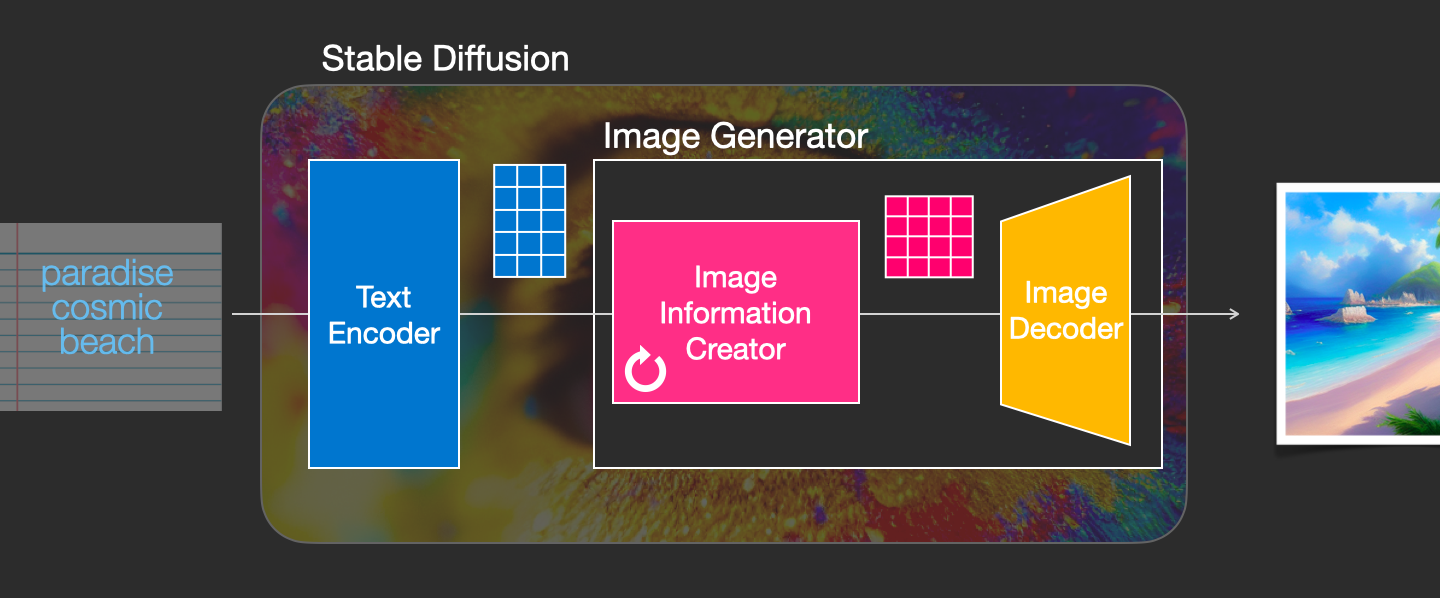 |
2- Image Decoder
The image decoder paints a picture from the information it got from the information creator. It runs only once at the end of the process to produce the final pixel image.
 |
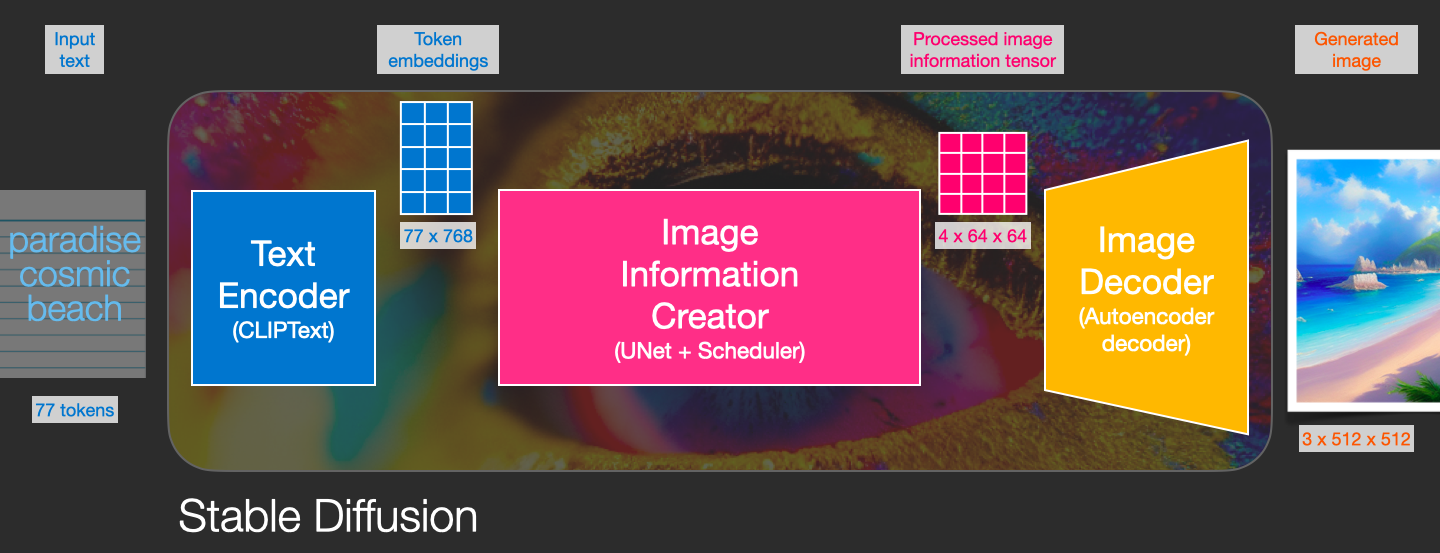
With this we come to see the three main components (each with its own neural network) that make up Stable Diffusion:
ClipText for text encoding.
Input: text.
Output: 77 token embeddings vectors, each in 768 dimensions.UNet + Scheduler to gradually process/diffuse information in the information (latent) space.
Input: text embeddings and a starting multi-dimensional array (structured lists of numbers, also called a tensor) made up of noise.
Output: A processed information arrayAutoencoder Decoder that paints the final image using the processed information array.
Input: The processed information array (dimensions: (4,64,64))
Output: The resulting image (dimensions: (3, 512, 512) which are (red/green/blue, width, height))
 |
What is Diffusion Anyway?
Diffusion is the process that takes place inside the pink “image information creator” component. Having the token embeddings that represent the input text, and a random starting image information array (these are also called latents), the process produces an information array that the image decoder uses to paint the final image.
 |
 |
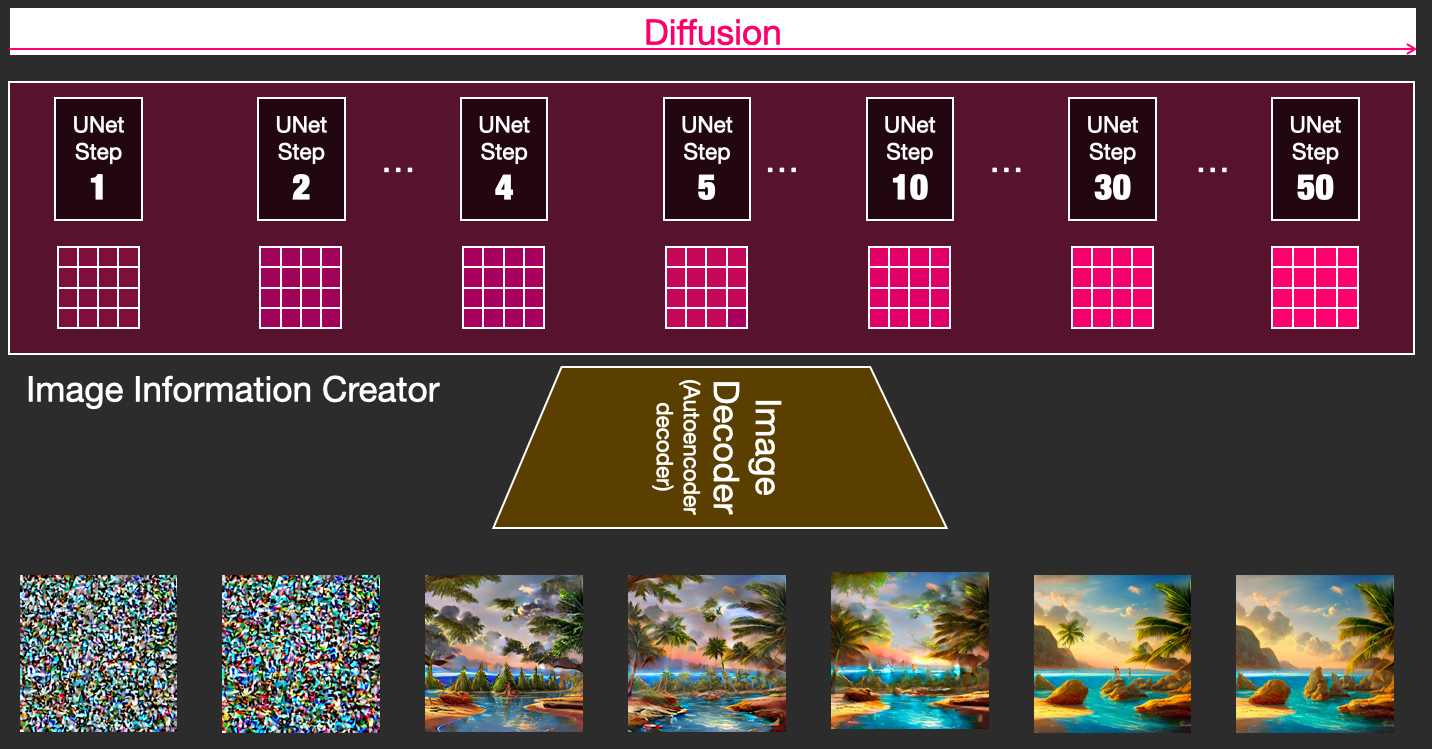 |
How diffusion works
The central idea of generating images with diffusion models relies on the fact that we have powerful computer vision models. Given a large enough dataset, these models can learn complex operations. Diffusion models approach image generation by framing the problem as following:
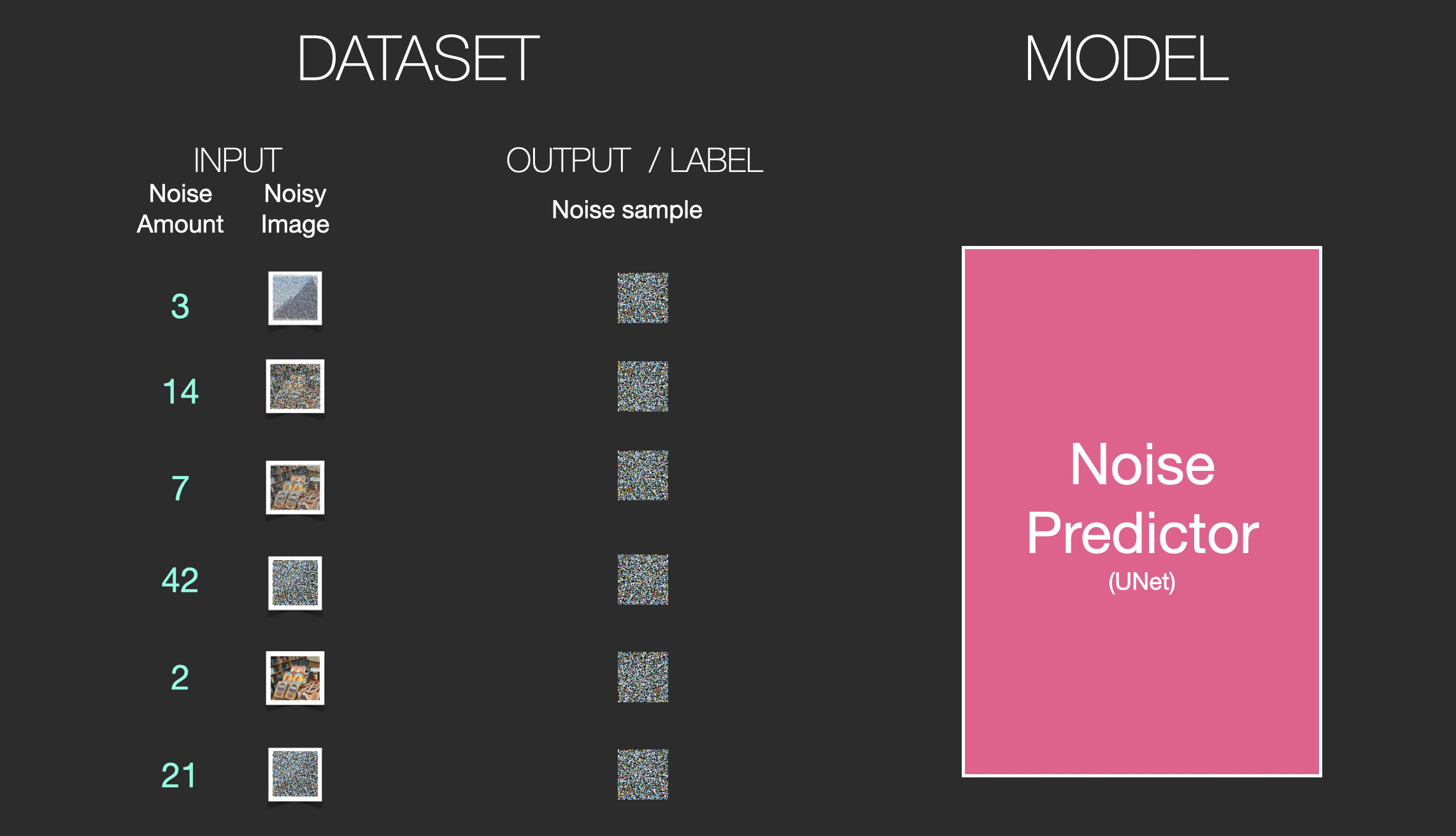
Say we have an image, we generate some noise, and add it to the image.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Let’s now see how this can generate images.
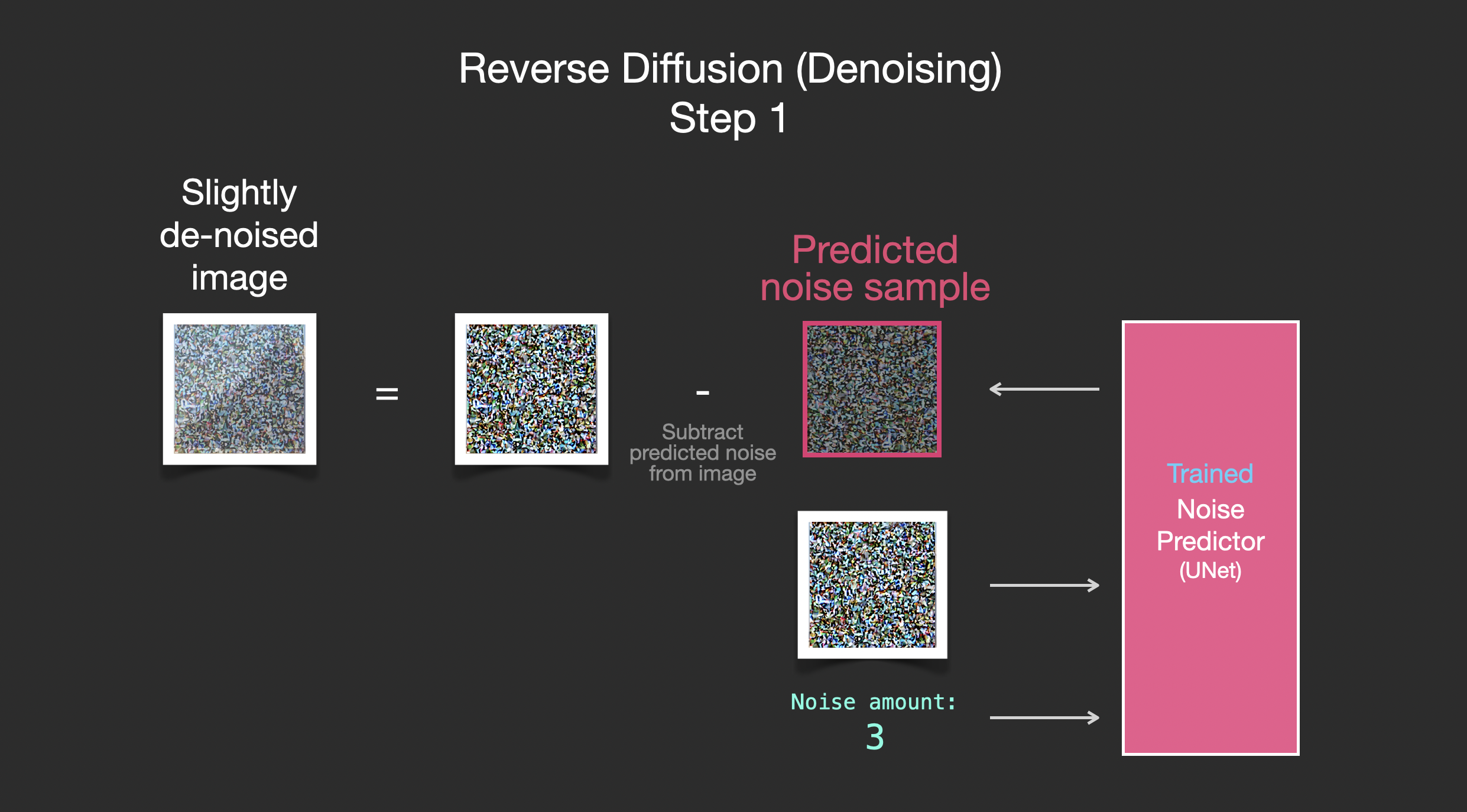
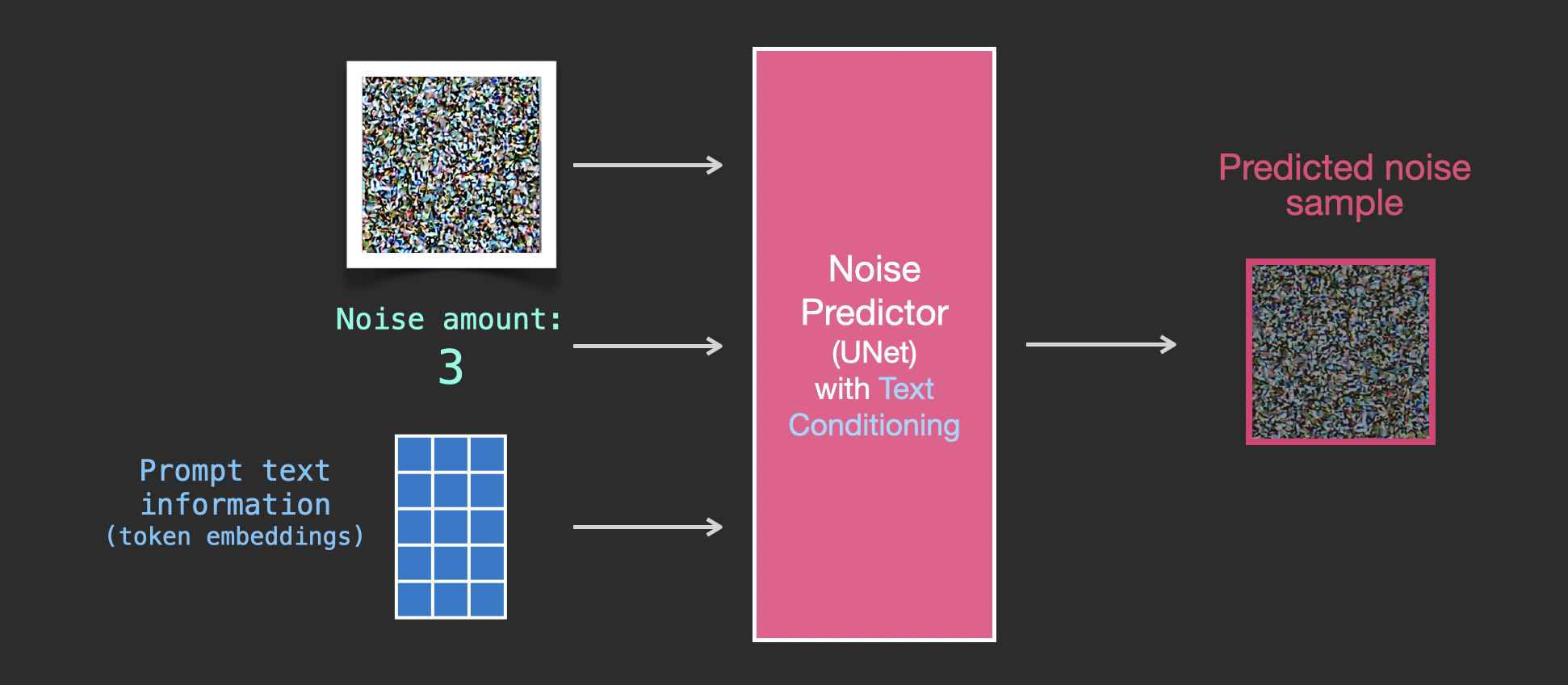
Painting images by removing noise
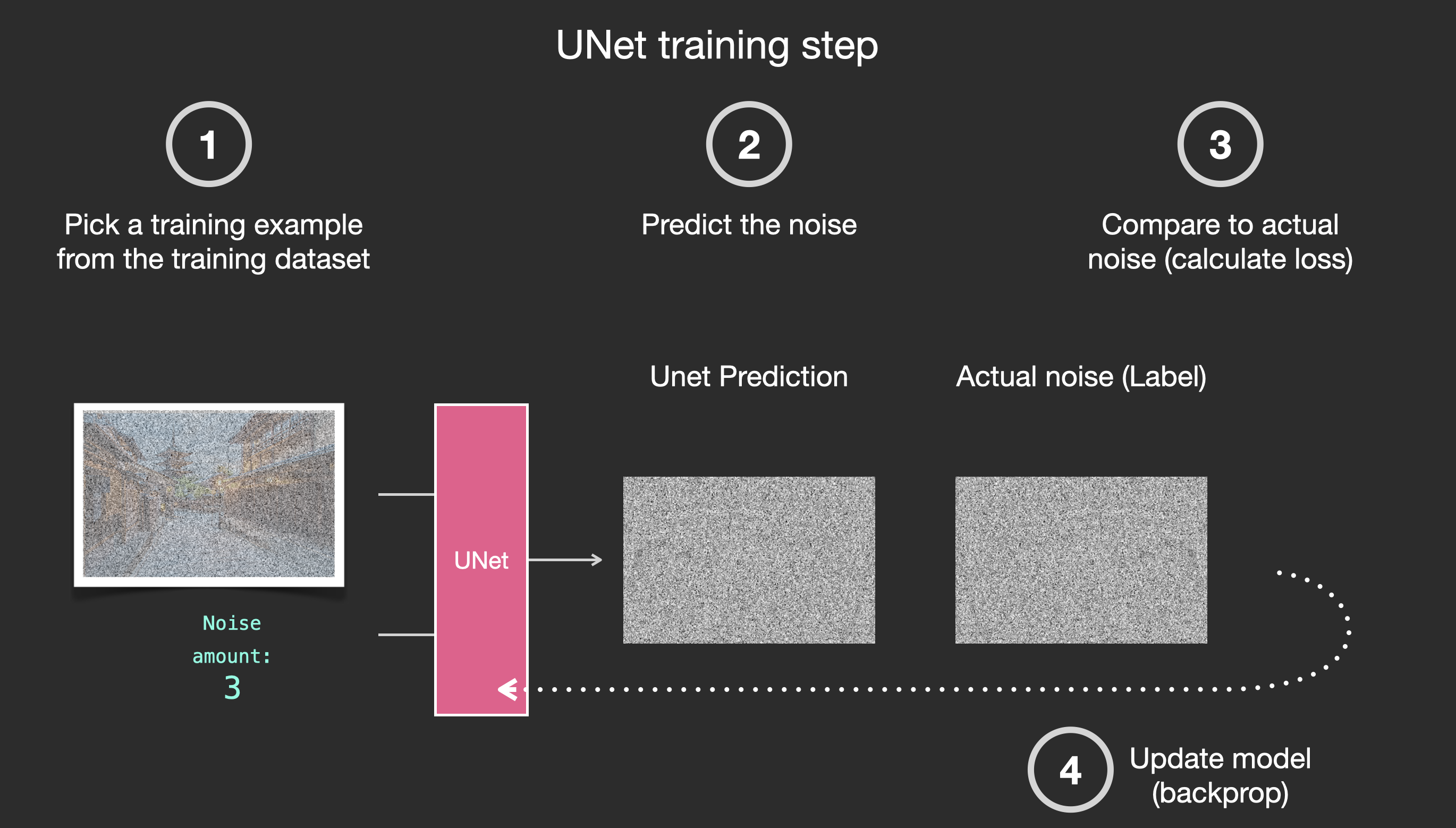
The trained noise predictor can take a noisy image, and the number of the denoising step, and is able to predict a slice of noise.
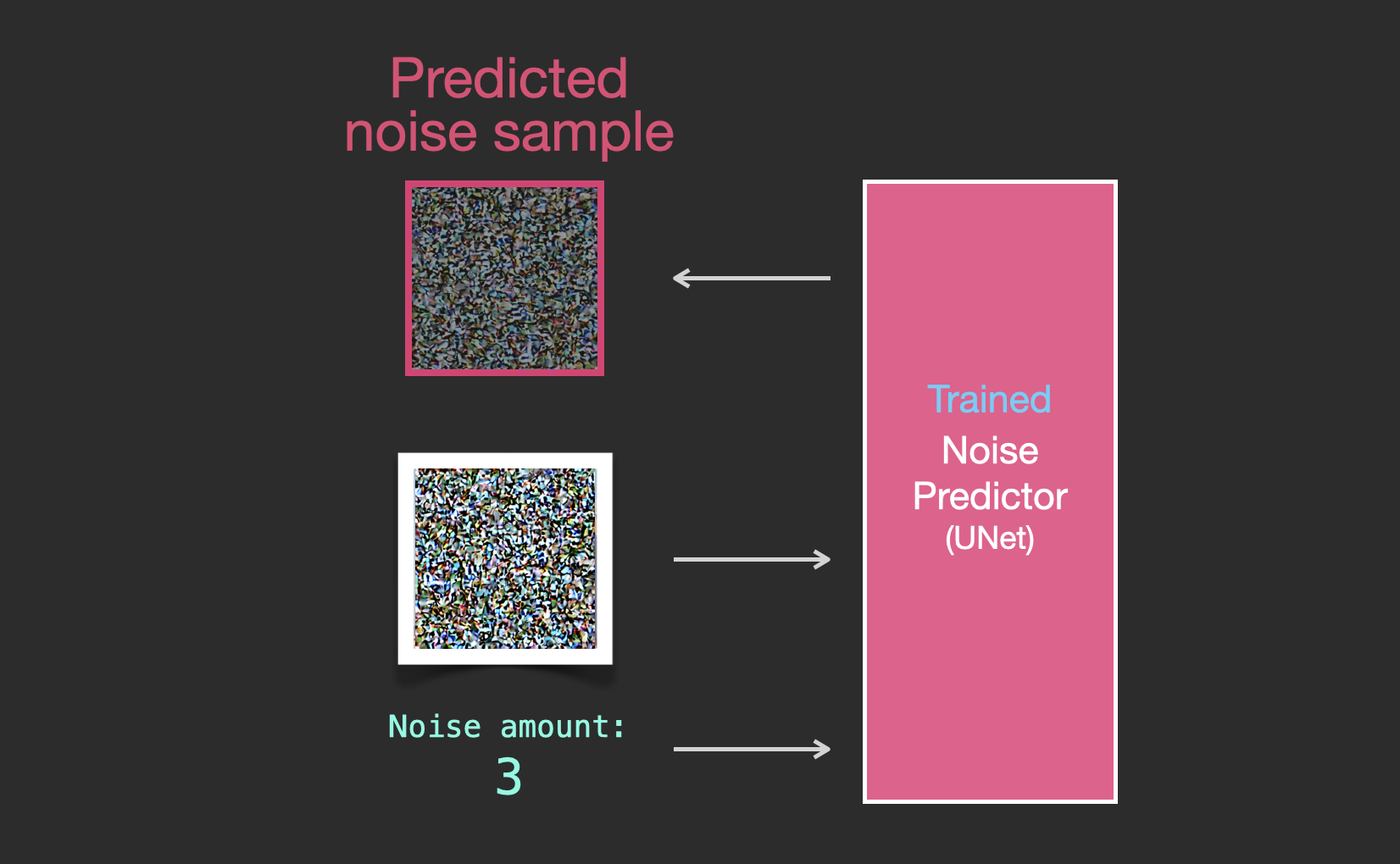 |
 |
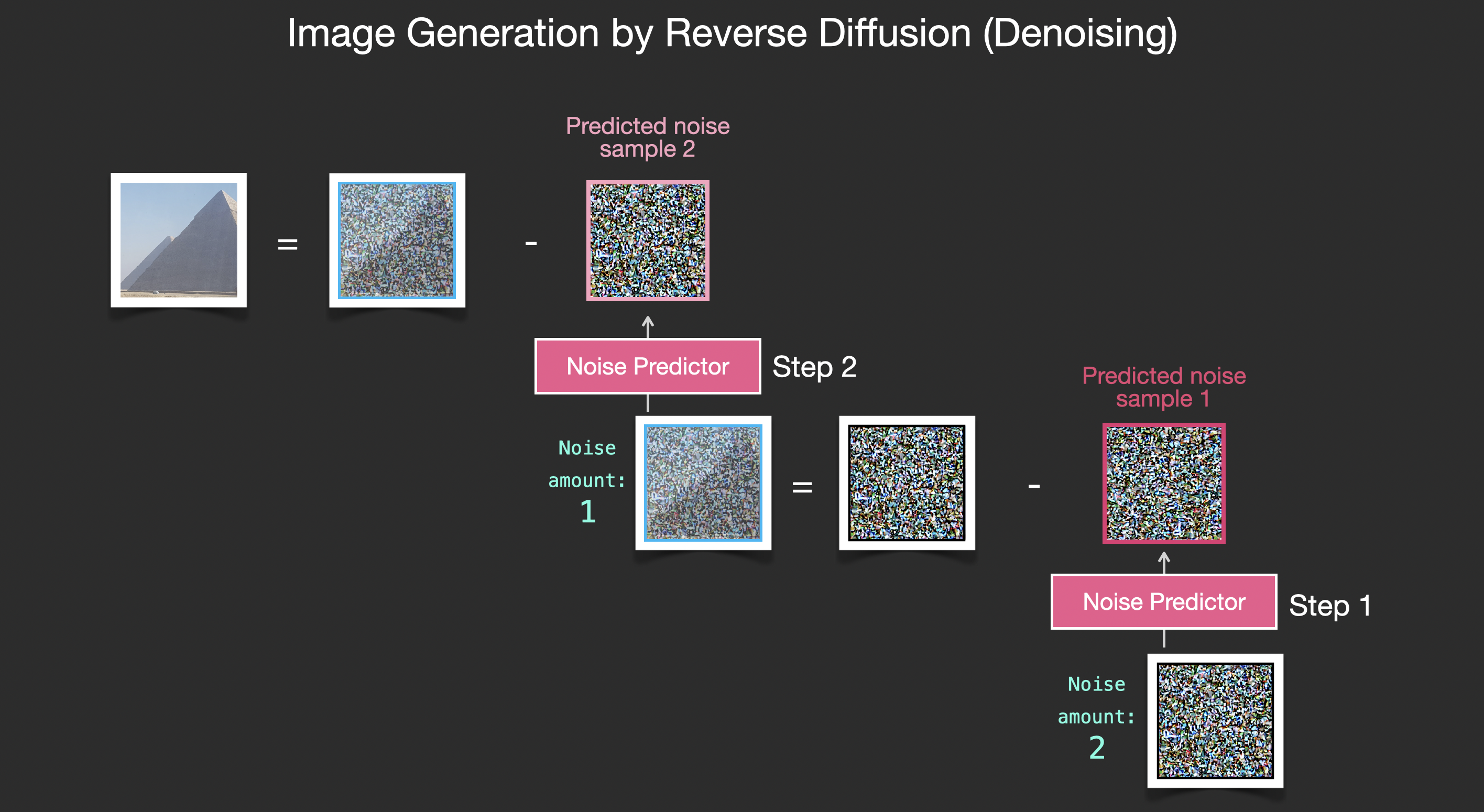 |
This concludes the description of image generation by diffusion models mostly as described in Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. Now that you have this intuition of diffusion, you know the main components of not only Stable Diffusion, but also Dall-E 2 and Google’s Imagen.
Note that the diffusion process we described so far generates images without using any text data. So if we deploy this model, it would generate great looking images, but we’d have no way of controlling if it’s an image of a pyramid or a cat or anything else. In the next sections we’ll describe how text is incorporated in the process in order to control what type of image the model generates.
Speed Boost: Diffusion on Compressed (Latent) Data Instead of the Pixel Image
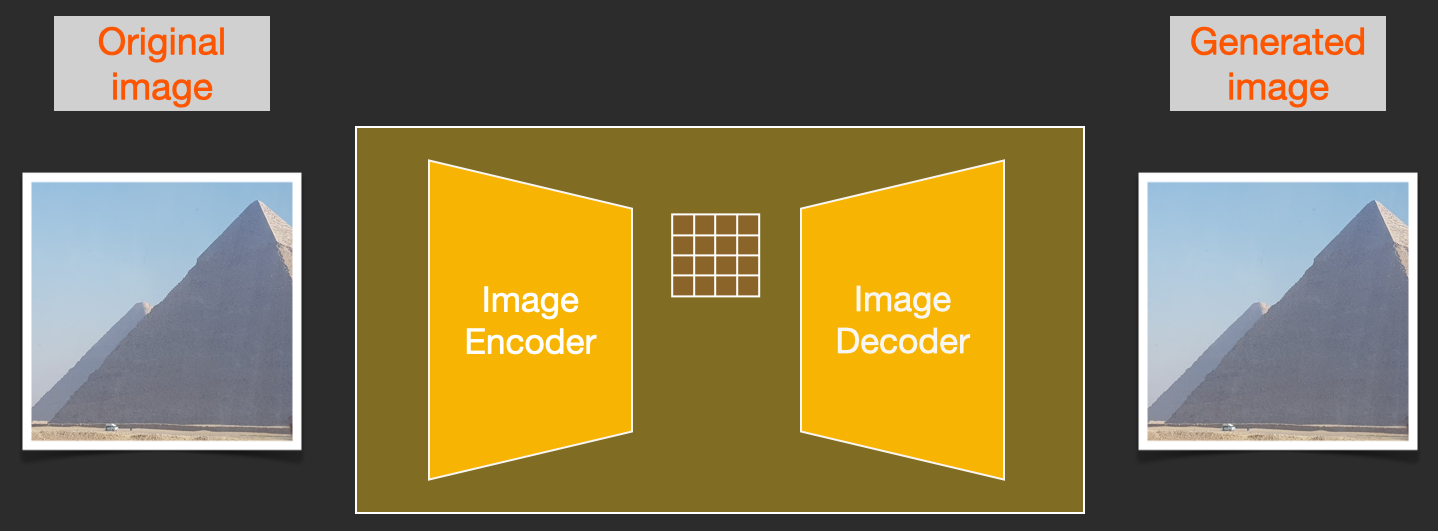
To speed up the image generation process, the Stable Diffusion paper runs the diffusion process not on the pixel images themselves, but on a compressed version of the image. The paper calls this “Departure to Latent Space”.
This compression (and later decompression/painting) is done via an autoencoder. The autoencoder compresses the image into the latent space using its encoder, then reconstructs it using only the compressed information using the decoder.
 |
 |
 |
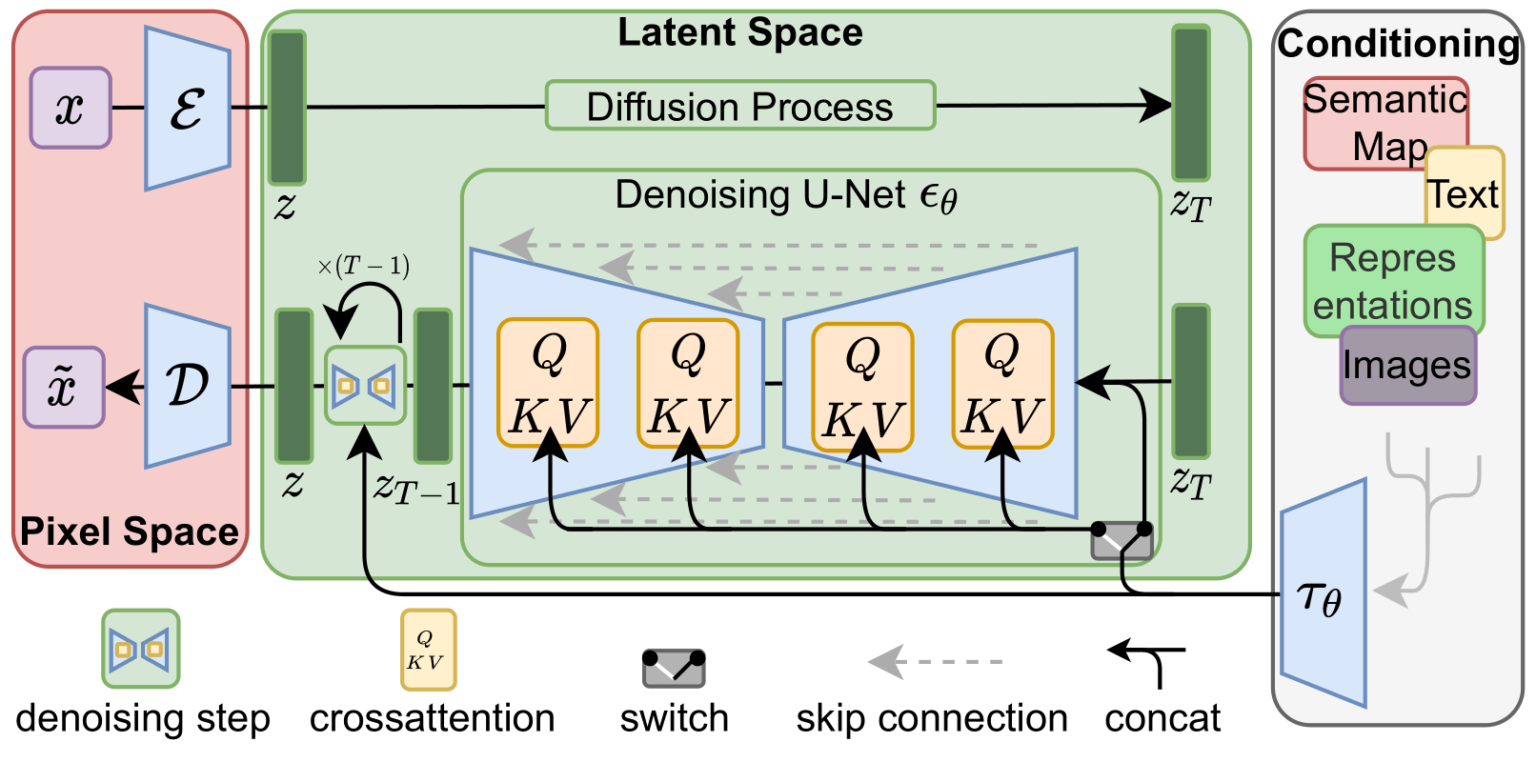 |
This figure additionally shows the “conditioning” components, which in this case is the text prompts describing what image the model should generate. So let’s dig into the text components.
The Text Encoder: A Transformer Language Model
A Transformer language model is used as the language understanding component that takes the text prompt and produces token embeddings. The released Stable Diffusion model uses ClipText (A GPT-based model), while the paper used BERT.
The choice of language model is shown by the Imagen paper to be an important one. Swapping in larger language models had more of an effect on generated image quality than larger image generation components.
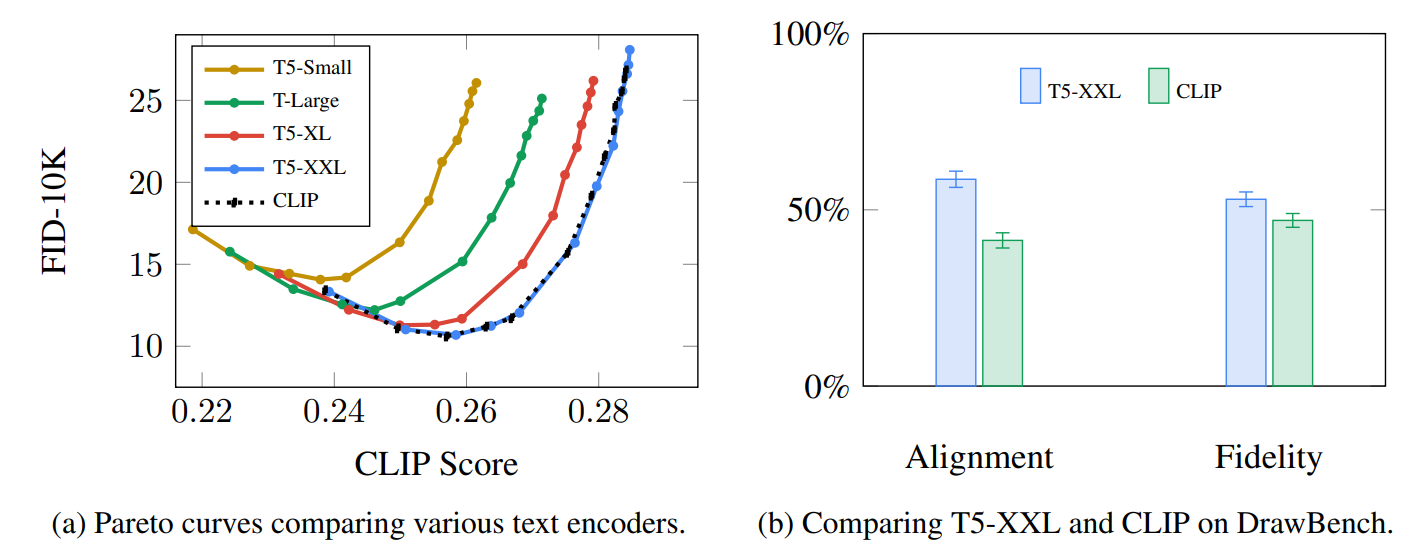 |
| Larger/better language models have a significant effect on the quality of image generation models. Source: Google Imagen paper by Saharia et. al.. Figure A.5. |
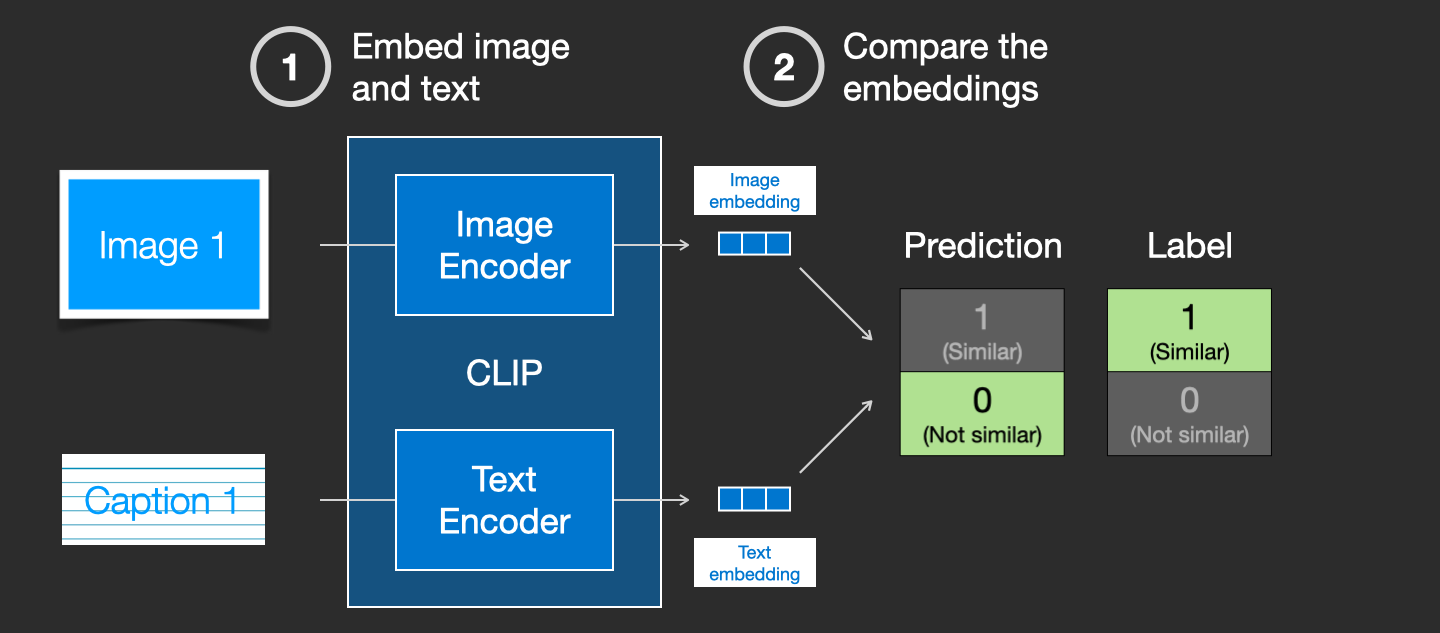
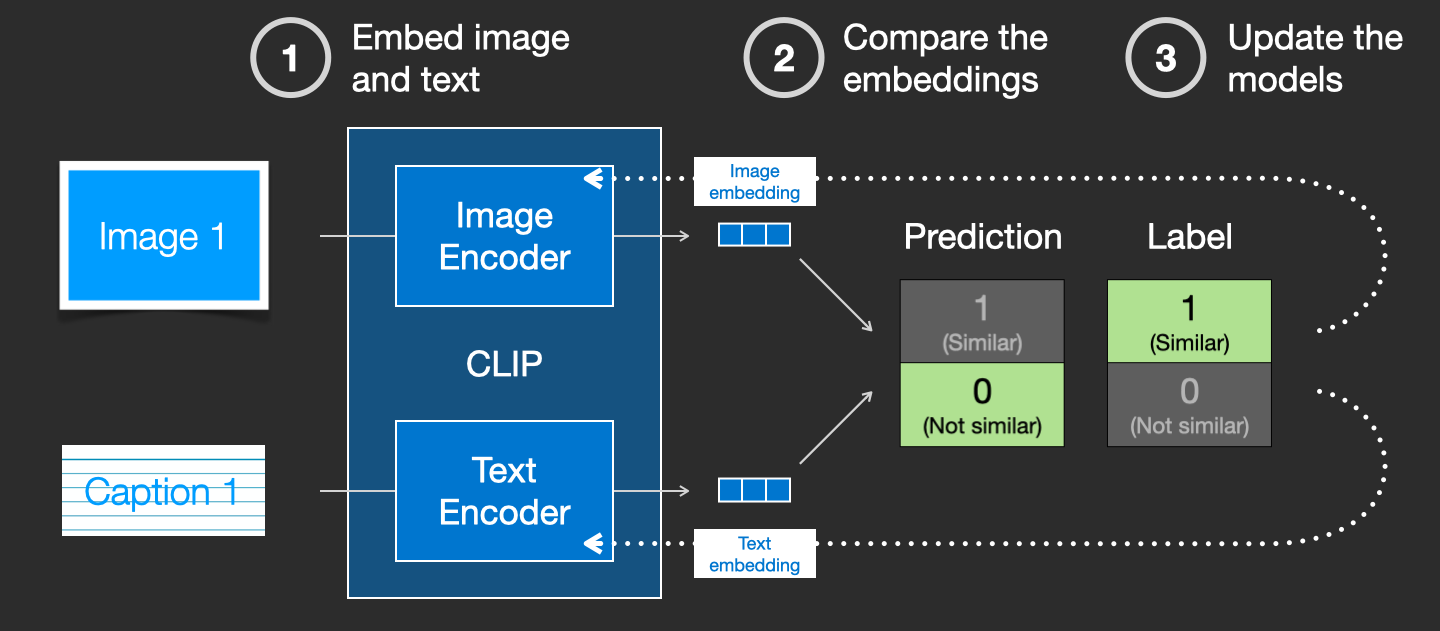
How CLIP is trained
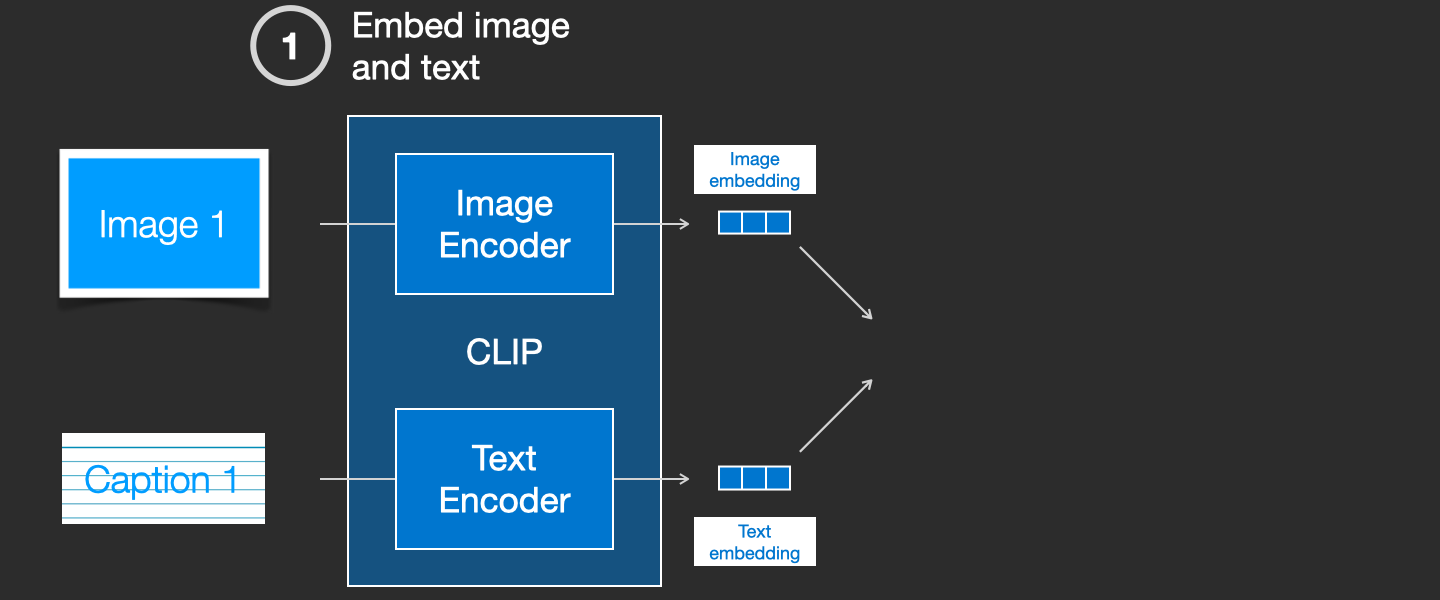
CLIP is trained on a dataset of images and their captions. Think of a dataset looking like this, only with 400 million images and their captions:
 |
In actuality, CLIP was trained on images crawled from the web along with their “alt” tags.
CLIP is a combination of an image encoder and a text encoder. Its training process can be simplified to thinking of taking an image and its caption. We encode them both with the image and text encoders respectively.
 |
 |
 |
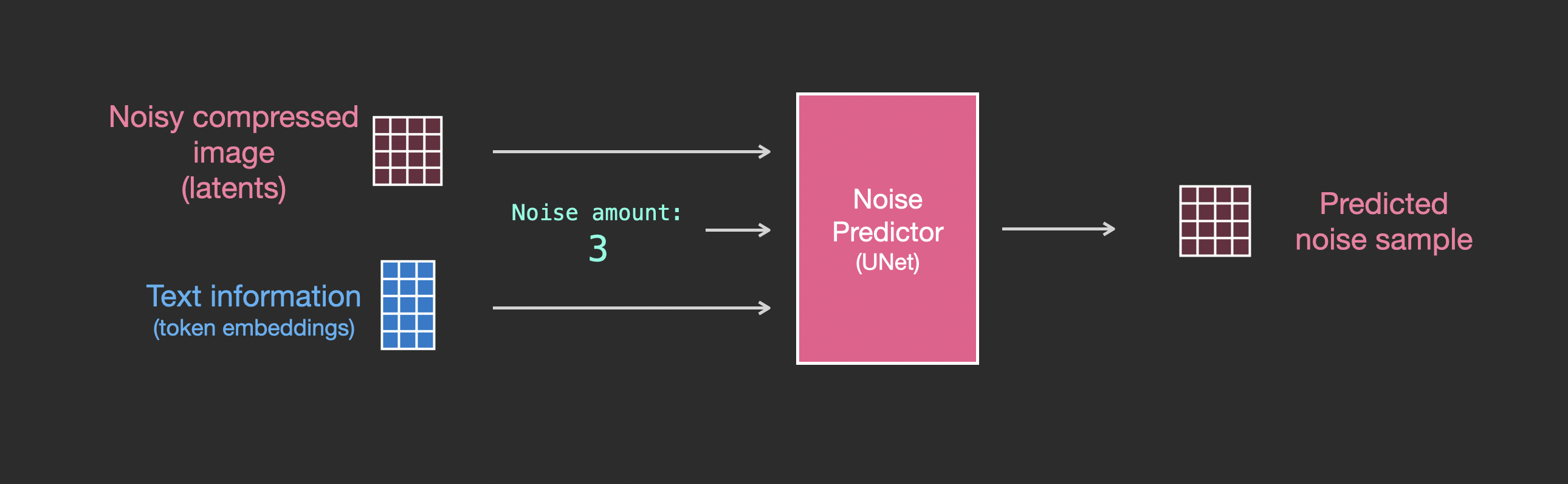
Feeding Text Information Into The Image Generation Process
To make text a part of the image generation process, we have to adjust our noise predictor to use the text as an input.
 |
 |
To get a better sense of how the text tokens are used in the Unet, let’s look deeper inside the Unet.
Layers of the Unet Noise predictor (without text)
Let’s first look at a diffusion Unet that does not use text. Its inputs and outputs would look like this:
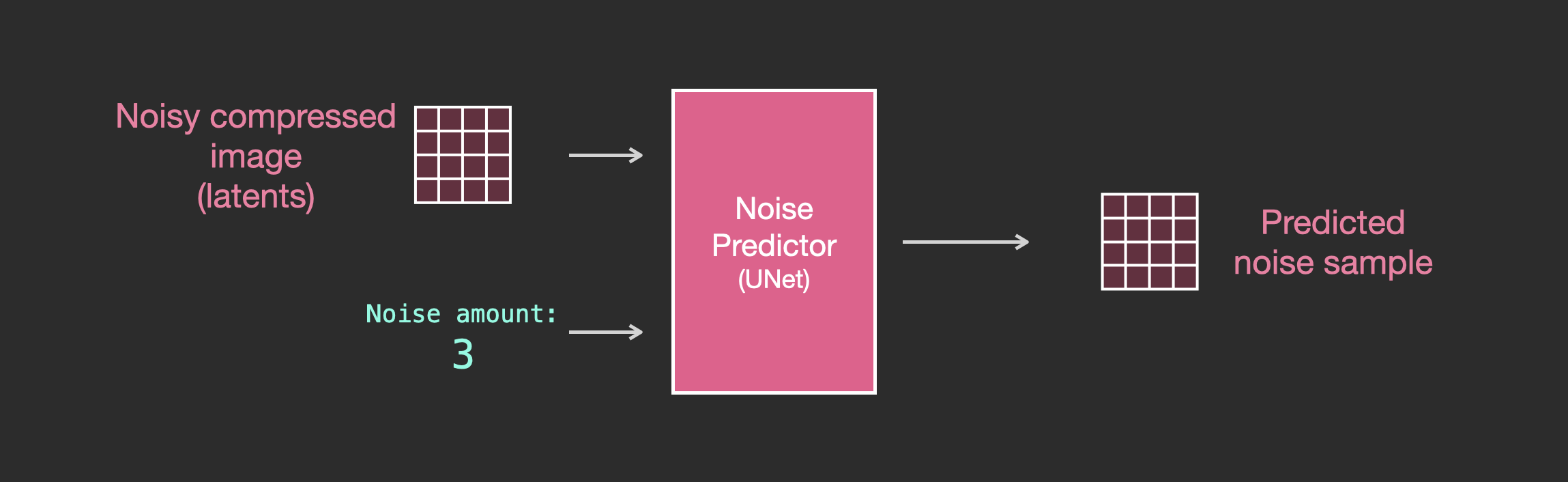 |
Inside, we see that:
- The Unet is a series of layers that work on transforming the latents array
- Each layer operates on the output of the previous layer
- Some of the outputs are fed (via residual connections) into the processing later in the network
- The timestep is transformed into a time step embedding vector, and that’s what gets used in the layers
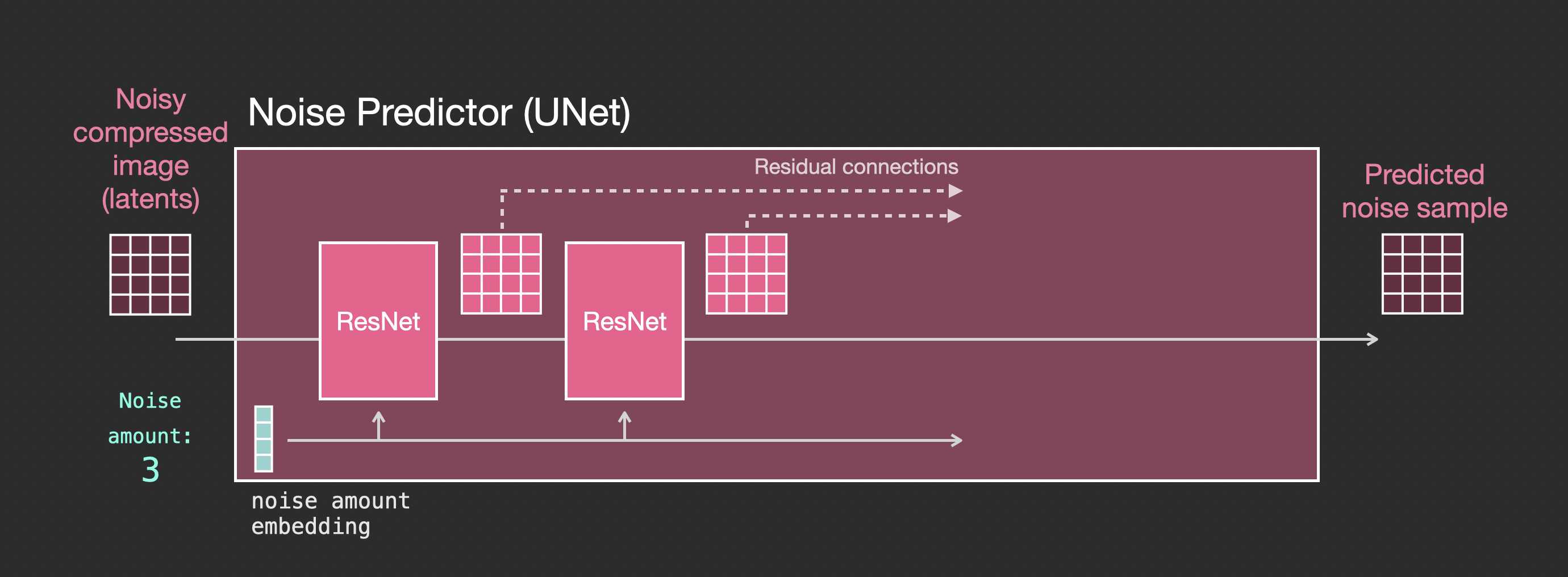 |
Layers of the Unet Noise predictor WITH text
Let’s now look how to alter this system to include attention to the text.
 |
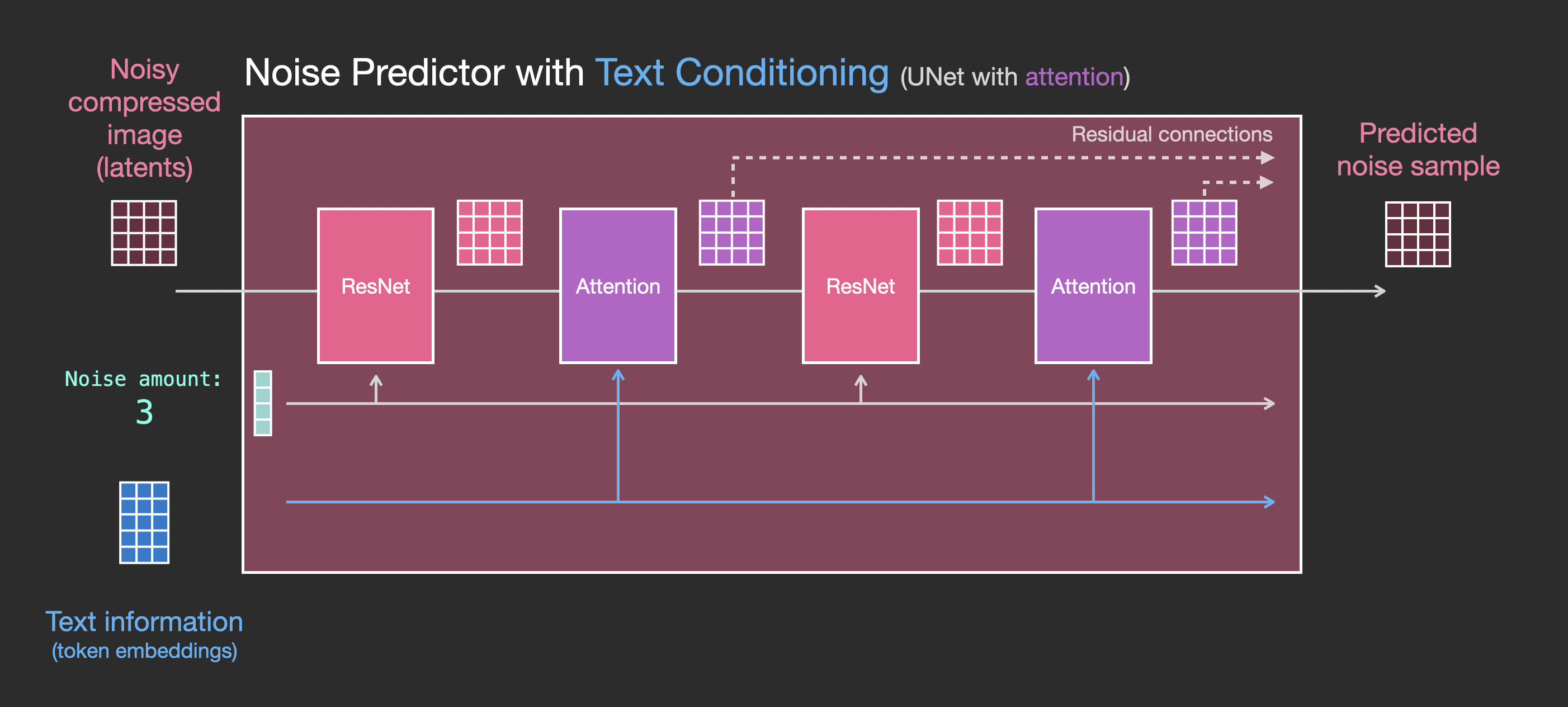 |
Note that the ResNet block doesn’t directly look at the text. But the attention layers merge those text representations in the latents. And now the next ResNet can utilize that incorporated text information in its processing.
Conclusion
I hope this gives you a good first intuition about how Stable Diffusion works. Lots of other concepts are involved, but I believe they’re easier to understand once you’re familiar with the building blocks above. The resources below are great next steps that I found useful.
Resources
- one-minute YouTube short on using Dream Studio to generate images with Stable Diffusion.
- Stable Diffusion with 🧨 Diffusers
- The Annotated Diffusion Model
- How does Stable Diffusion work? – Latent Diffusion Models EXPLAINED [Video]
- Stable Diffusion - What, Why, How? [Video]
- High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models [The Stable Diffusion paper]
- For a more in-depth look at the algorithms and math, see Lilian Weng’s What are Diffusion Models?
- Watch the great Stable Diffusion videos from fast.ai
